Answer:
![ksp = [Cl^(-1) ]^2 * [Pb^+1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c8l3qvyafm1htqgtyh8cqmomk1p26mppgr.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
The ksp is the constant of the product of solubility (it tells us that so much substance is going to dissolve and that this is constant), it is like the constants of equilibrium (equation 1). This is the concentration of the products (C and D) divided into the concentration of the reagents (A and B) raised to their stoichiometric coefficients (a, b, c, d).
Reaction 1.
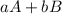 ⇒
⇒
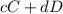
Equation 1.
![K = ([C]^c* [D]^d)/([A]^a*[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/f2ilyh1yei88t0n27mq2yzllffxe6f98fa.png)
In this case the reagents are a salt in solid state - PbCl2(S) - this will not be taken into account in the expression of Ksp (neither liquids, nor solids are taken into account) only the substances in gaseous state (g) or in dissolution (aq). In the products there are two moles of ions
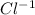 (aq) therefore its expression in ksp is
(aq) therefore its expression in ksp is
![[Cl^(-1)]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9rdlqsrhsvm1h82lrx32hvi8zmv6p27pyh.png) and of ions
and of ions
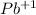 there is a mole and in the expression will be
there is a mole and in the expression will be
![[Pb^(+1)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/1trbj0p8g4mz058qi49uy678reopfzsg3g.png) . According to the above the expression of ksp is:
. According to the above the expression of ksp is:
![ksp = [Cl^(-1) ]^2 * [Pb^+1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c8l3qvyafm1htqgtyh8cqmomk1p26mppgr.png)