Answer:
x = 6; this is an extraneous solution.
Explanation:
The equation we are given is
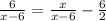
First we will simplify the constant. 6/2 = 3; this gives us
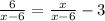
Next, we will multiply all terms by (x-6) in order to eliminate the denominator:
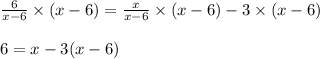
Using the distributive property, we have:
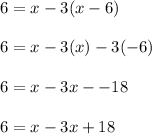
Combining like terms on the right, we have
6 = -2x + 18
Subtract 18 from each side:
6-18 = -2x+18-18
-12 = -2x
Divide both sides by -2:
-12/-2 = -2x/-2
6 = x
However, if we were to use 6 for x, this would give us 0 in the denominators; thus it is an extraneous solution.