The transformation is isobaric (constant pressure), so the work done by the gas is the product between its pressure and the variation of volume:
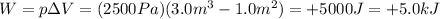
The heat transferred to the gas is
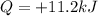
So we can use the first law of thermodynamics to compute the variation of internal energy of the gas:
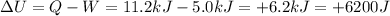
where the positive sign means the internal energy of the gas has increased.