A vector has length (magnitude) and direction.
Multiplying a vector by a scalar can alter both its length and its direction.
Specifically, you are multiplying by
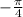
.
When you multiply a vector by a negative as in this case the direction changes.
Next when we multiply by a quantity greater than 1 the vector's length increases. When we multiply by a quantity less than 1 the vector's length decreases. Here you are multiplying by a quantity less than 1. For the sake of getting an estimate pi is approximately 3.14 so dividing that by 4 gives you a quantity less than 1.
So multiplying by
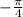
will have the following effects on the vector:
It will face the opposite direction and it will be shorter (have less magnitude). Specifically the magnitude will be
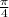
of what it was before.