The value of the discriminant is the value of
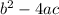
located inside the square root of the quadratic formula. To find this, we simply look at the quadratic equation in standard form:
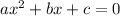
and plug in the existing values into the quadratic formula (
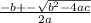
. Plug in the values of a b and c (2, 7, and -4, respectively) and get
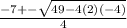
.
Simplifying this, we get
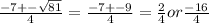
which equal 1/2 and -4, respectively.
A )The value of the discriminant is 81 (see work above)
B ) 2 solutions, discriminant is positive, and not equal to zero. They are both rational since sqrt 81 is a rational number
C ) 1/2 and -4 (see work above)