Answer: The number of moles of carbon dioxide produced are
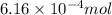 and the mass of calcium carbonate is 61.6 mg
and the mass of calcium carbonate is 61.6 mg
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles of carbon dioxide gas, we use the equation given by ideal gas which follows:
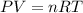
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 738.0 mmHg
V = Volume of the gas = 15.5 mL = 0.0155 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
T = Temperature of the gas =
![25^oC=[25+273]K=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/vrqkyyitu3rpnlky8usokrw46hqm7gl9o0.png)
R = Gas constant =
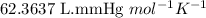
n = number of moles of carbon dioxide gas = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:

For the given chemical equation:
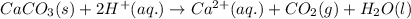
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of carbon dioxide gas is produced from 1 mole of calcium carbonate
So,
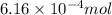 of carbon dioxide will be produced from =
of carbon dioxide will be produced from =
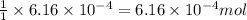 of calcium carbonate
of calcium carbonate
- To calculate the mass for given number of moles, we use the equation:
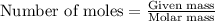
Molar mass of calcium carbonate = 100 g/mol
Moles of calcium carbonate =
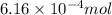
Putting values in above equation:
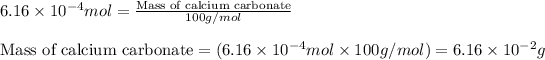
Converting this into milligrams, we use the conversion factor:
1 g = 1000 mg
So,
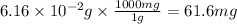
Hence, the number of moles of carbon dioxide produced are
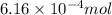 and the mass of calcium carbonate is 61.6 mg
and the mass of calcium carbonate is 61.6 mg