Step-by-step explanation:
It is known that the relation between pH and hydrogen ion concentration is as follows.
pH =
![-log [H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/n70pj7jbxi0d7x31k6g48qds60ogu6bep8.png)
3 =
![-log [H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/n70pj7jbxi0d7x31k6g48qds60ogu6bep8.png)
antilog (-3) =
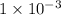
![[H^(+)] = 1 * 10^(-3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/thvr35n90dxar78xan5mnr41pa0m7cf8sv.png) M
M
Now, let the given acid is HA and it dissociates as follows.
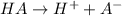
0.1 0 0
0.1 - x x x
We know that relation between
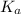 ,
,
![[H^(+)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/75vk4lm3dg3i0qv728qhnrrb5qib1loutc.png) and HA is as follows.
and HA is as follows.
![K_(a) = ([H^(+)][A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/2mrqlpw0wduypxy0mkkntd9nmpmygdvdu4.png)
=
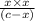
=
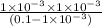
=
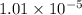
Also,
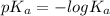
=
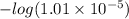
= 5.00
Thus, we can conclude that the
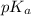 of given acid is 5.0.
of given acid is 5.0.