Answer : The pressure when the gas occupies a volume of 3.3 L is, 25.6 atm.
Explanation :
According to the Boyle's law, the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume of the gas at constant temperature of the gas and the number of moles of gas.
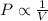
or,
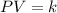
or,
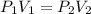
where,
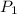 = initial pressure of the gas = 6.5 atm
= initial pressure of the gas = 6.5 atm
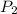 = final pressure of the gas = ?
= final pressure of the gas = ?
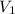 = initial volume of the gas = 13 L
= initial volume of the gas = 13 L
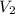 = final volume of the gas = 3.3 L
= final volume of the gas = 3.3 L
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get the final pressure of the gas.
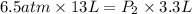
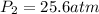
Therefore, the pressure when the gas occupies a volume of 3.3 L is, 25.6 atm.