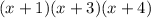Answer:
Option A.
Explanation:
Polynomial is an equation of the form
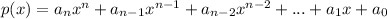 where
where
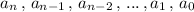 are the coefficients such that
are the coefficients such that
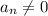
Let
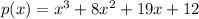
For
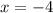 ,
,
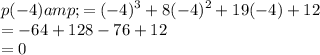
So, x+4 is a factor of p(x) .
{we know that x-a is a factor of p(x) if and only if p(a)=0}
Consider the following:
![p(x)=x^3+8x^2+19x+12\\=x^2(x)+8x(x)+19x+12\\=x^2(x+4)+8x(x+4)+19(x+4)-4x^2-32x-76+12\\=(x+4)(x^2+8x+19)-4x^2-32x-64\\=(x+4)(x^2+8x+19)-4x(x+4)-32(x+4)+16x+128-64\\=(x+4)(x^2+8x+19-4x-32)+16(x+4)+64-64\\=(x+4)(x^2+4x-13+16)\\=(x+4)(x^2+4x+3)\\=(x+4)(x^2+3x+x+3)\\=(x+4)\left [ x(x+3)+1(x+3) \right ]\\=(x+1)(x+3)(x+4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/bl57nyow6w8mrvuhdbqrraugpqfhkkyidh.png)
So, complete factorisation of p(x) is