Answer:
2.
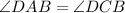
Explanation:
We have been given a diagram of a quadrilateral ABCD with diagonal BD bisecting angle ADC, which means that
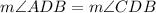 .
.
We can see that diagonal BD has divided quadrilateral ABCD into two triangles. We can see that in triangles ADB and CDB side AD equals to side CD and side BD equals to itself, therefore, triangles ADB and CDB are congruent by SAS postulate of congruence.
Since triangle ADB is congruent to triangle CDB, therefore, all sides and angles of triangle ADB will be congruent to corresponding sides and angles of triangle CDB.
Let us see which of our given options represent corresponding angles of both triangles.
1.

We can see from our diagram that angle DAB corresponds to angle DCB, therefore, 1st equation is not true.
2.
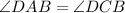
We can see from our diagram that angle DAB corresponds to angle DCB, therefore, 2nd equation is true.
3.
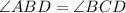
We can see from our diagram that angle CBD corresponds to angle ABD, therefore, 3rd equation is not true.
4.
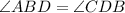
We can see from our diagram that angle CDB corresponds to angle ADB, therefore, 4th equation is not true.