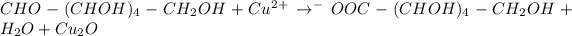Answer:
Gluconic acid is formed when Benedict's reagent is reduced by glucose or galactose.
Step-by-step explanation:
Benedict's reagent: Alkaline solution of copper sulfate , sodium citrate and sodium carbonate
Glucose and galactose both are reducing sugar. Both of them reduces copper(II) ion in Benedict's reagent into copper (I) ion.
During this reaction glucose or galactose gets converted into gluconic acid and red precipitate of copper (I) oxide is obtained along with formation of water.