Answer:- There are
 particles in the container present at 23 degree C and 101.3 pKa.
particles in the container present at 23 degree C and 101.3 pKa.
Solution:- The given volume of the container is 4.0 L at 23 degree C and 101.3 kPa pressure.
We would calculate the moles using ideal gas law equation(PV = nRT) and then the moles are converted to particles on multiply the moles by Avogadro number.
Let's convert degree C to kelvin and pKa to atm.
T = 23 + 273 = 296 K
P = 101.3 pKa = 1 atm
R =
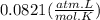
V = 4.0 L
n = ?
Let's plug in the values in the equation:
1(4.0) = n(0.0821)(296)
4.0 = n(24.3)
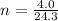
n = 0.165 mol
Let's multiply the moles by Avogadro number to get the number of particles:
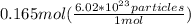
=
 particles
particles
So, from above calculations there would be
 particles in the container.
particles in the container.