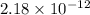Answer: The base dissociation constant for a conjugate base is
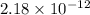
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the base dissociation constant for the given acid dissociation constant, we use the equation:
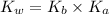
where,
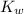 = Ionic product of water =
= Ionic product of water =
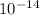
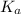 = Acid dissociation constant =
= Acid dissociation constant =
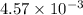
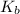 Base dissociation constant = ?
Base dissociation constant = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
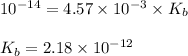
Hence, the base dissociation constant for a conjugate base is