Answer:
Resistivity = 231.481 K Ohm
Yes, Intrinsic Silicon is the semiconductor.
Step-by-step explanation:
Solution:
At 300K:
Let suppose mobility of electron in intrinsic semiconductor =
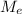
Mobility of electron in intrinsic semiconductor is:
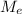 = 1300
= 1300
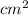 /volt.sec
/volt.sec
Let suppose mobility of hole in intrinsic semiconductor =
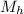
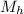 = 500
= 500
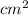 /volt.sec
/volt.sec
We know that, intrinsic silicon semiconductor has equal number of holes and electrons. So,
At 300 K
Intrinsic Carrier Concentration = 1.5 x
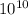 /
/
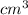 = C
= C
And,
Conductivity of intrinsic Silicon is:
σ = C x (
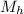 +
+
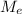 ) e
) e
e = 1.6 x
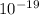 C
C
So, plugging in the values, we get:
σ = C x (
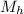 +
+
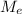 ) e
) e
σ = 1.5 x
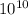 x (500 + 1300) x 1.6 x
x (500 + 1300) x 1.6 x
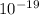
σ = 4.32 x
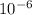
So, now we can find the resistivity.
Resistivity = 1/σ
Resistivity = 1/ 4.32 x
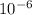
Resistivity = 231.481 K Ohm
Yes, Intrinsic Silicon is the semiconductor.