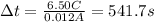The current intensity is defined as the amount of charge Q that passes through a certain point of an electrical wire in a time interval of
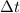
:
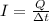
In our problem, the current intensity is
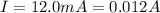
while the amount of charge that passes a certain point of the wire is
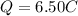
If we re-arrange the previous equation:
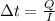
we can find the time needed for this amount of charge to pass through a point of the wire: