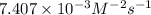Answer : The rate constant of a reaction is,
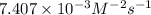
Solution :
The general rate law expression is,
![rate=k[A]^m[B]^n](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/ddbvxmkr2pojxa4swq68qy0a25gcyznowo.png)
where,
k = rate constant
[A] and [B] are the concentrations
m is the order of reactant A and n is the order of reactant B
Now put all the given values in the above rate law expression, we get the value for rate constant.
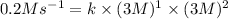
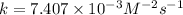
Therefore, the rate constant of a reaction is,