Answer:- Molarity of the glucose solution is 0.1M.
Solution:- Molarity is moles of solute per liter of the solution.
From given info, 36.0 grams of glucose are present in a 2.0 L solution. We need to convert the grams to moles using molar mass and then divide the moles by the liters to get the molarity.
First step, grams to moles conversion:
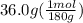
= 0.2 mol
Second step, calculations for molarity:
molarity =
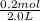
= 0.1M
(where, M stands for molarity)
So, the molarity of the glucose solution is 0.1M.