Answer: Two.
Explanation: Number of ionization constants associated with an acid equals to the number of hydrogen ions(protons) that it produces in aqueous solution.
For example, HCl is a monoprotic acid as it produces only one hydrogen ion in aqueous solution and so only one ionization constant is associated with it.
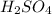 (sulfuric acid) is a diprotic acid as it produces two hydrogen ions in aqueous solution and hence there are two ionization constant values associated with this.
(sulfuric acid) is a diprotic acid as it produces two hydrogen ions in aqueous solution and hence there are two ionization constant values associated with this.
Similarly, Oxalic acid is also a diprotic acid and so two ionization constant values are associated with this.
The two ionization equations of oxalic acid are as follows:-
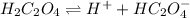
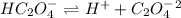
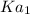 and
and
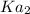 are the two ionization constants for first and second equations respectively.
are the two ionization constants for first and second equations respectively.