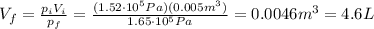First we need to convert everything into SI units.
The initial volume of the gas is (keeping in mind that
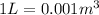
:
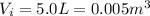
The initial pressure of the gas is (keeping in mind that
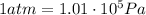
:
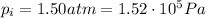
The final pressure of the gas is (keeping in mind that
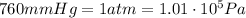
)
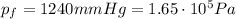
At constant temperature, the product between pressure and volume of the gas is constant, so we can write
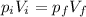
from which we find the final volume of the gas: