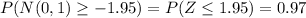We need to calculate the probability:
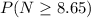
wherein N is the normal law.
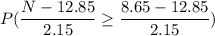
Simplifying the right hand side of the inequality we get:
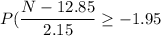
The above formula can be written in the form:
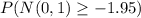
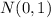
is the normal law with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
Using the table of the values we find the probability