First, let's calculate the initial and final speed of the spaceship:
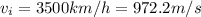
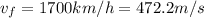
By using the initial and final speed, we can calculate the acceleration of the spaceship:
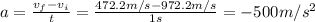
where the negative sign means it is directed against the motion of the spaceship (in fact, the spaceship is decelerating).
And now, by using Newton's second law:
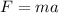
we can calculate the net force that acted on the spaceship:
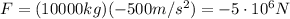
where the negative sign means it is directed against the direction of motion of the spaceship.