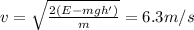We can solve the problem by using the law of conservation of energy.
Using the ground as reference point, the mechanical energy of the brick when it is at 5 m from the ground is just potential energy (because the brick is initially at rest, so it doesn't have kinetic energy):
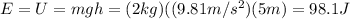
when the brick is at h'=3 m from the ground, its mechanical energy is now sum of kinetic energy and potential energy:

where v is the velocity of the brick. Since E is conserved, it must be equal to the initial energy (98.1 J), so we can solve this equation to find v: