Answer:
Hence, they will intersect at positive x-coordinates.
Explanation:
We are given two functions f(x) and g(x) as:
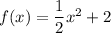 and
and
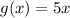 .
.
As the table of values for g are given as:
x g(x)
1 5
2 10
3 15
so on solving for g(x) using two point.
Let g(x)=y
We use the slope intercept form as:
y=mx+c
where m is the slope of line and c is the y-intercept of the line.
now for x=1 ,y=5
5=m+c
and for x=2, y=10
10=2m+c
on solving the above two equations using method of elimination we have:
m=5 and c=0
Hence, g(x)=5x
Now we can see by solving the equation f(x)=g(x) i.e. by solving a quadratic equation formed by equating f(x) and g(x) that the graph intersects at x=0.4174 and x=9.5826.
(since by solving
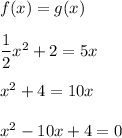 and hence solving this quadratic equation).
and hence solving this quadratic equation).
Hence, they will intersect at positive x-coordinates.