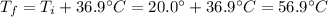When we add a certain amount of heat Q to a substance, the temperature of the substance increases by a

given by
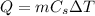
where m is the mass of the substance and Cs is the specific heat capacity of the substance.
By re-arranging the formula, we find
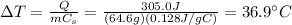
So, since the initial temperature of the metal is Ti=20 C, the final temperature is