(a) The beam contains
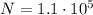
doubly charged positive ions per cubic centimeter. Each ion has a charge equal to 2 protons, so the total charge contained in 1 cubic centimeter is the number of ions times 2 times the charge of 1 proton:
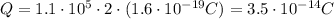
1 cubic centimeter corresponds to
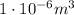
, so the charge density is equal to

So now we can calculate the magnitude of the current density, which is given by
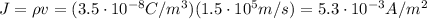
(b) Since the charges are positive, then the direction of the current density is equal to the direction of the velocity v.
(c) The current density is also equal to the ratio between the current I and the cross-sectional area A:
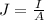
So, in order to find the current I, we also need the cross-sectional area A of the beam.