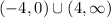Answer:
The intervals of increase are
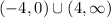
Explanation:
When a function is increasing, its derivative is positive. So if we want to find the intervals where a function increases, we differentiate it and find the intervals where its derivative is positive.
Let's find the intervals where
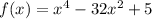 is increasing.
is increasing.
First, we differentiate f(x)
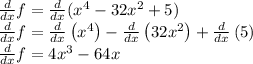
Now we want to find the intervals where
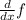 is positive This is done using critical points, which are the points where
is positive This is done using critical points, which are the points where
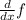 is either 0 or undefined.
is either 0 or undefined.
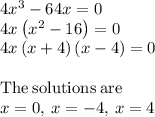
These points divide the number line into four intervals
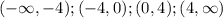
Let's evaluate
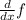 at each interval to see if it's positive on that interval.
at each interval to see if it's positive on that interval.
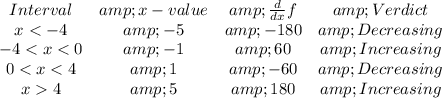
The intervals of increase are