The
correct answer is:
0.8558.
Step-by-step explanation:
The weights could be higher or lower than the mean by 52 grams.
Our formula for a z-score is:
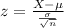
We have the variance instead of the standard deviation. Variance is the square of the standard deviation; to find the standard deviation, we take the square root:
√84681 = 291 = σ
We already have X-μ; this is 52 or -52. This gives us two z-scores:
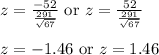
Using a z-table, the area under the curve to the left of (less than) -1.46 is 0.0721.
The area under the curve to the left of (less than) 1.46 is 0.9279.
We want the area between these two scores, since the difference between the weight and the mean could be less than or equal to 52; this means we subtract these probabilities:
0.9279-0.0721 = 0.8558.