Answer: The type of dilation is (A) Expansion.
Step-by-step explanation: As given in the question, the pre-image triangle OAB and the dilated image triangle O'A'B' are shown in the attached figure.
The vertices of ΔOAB are O(0, 0), A(-3, 3) and B(-2, -1).
The vertices of ΔO'A'B' are O'(0, 0), A'(-9, 9) and B'(-6, -3).
Since the directions of both the triangles are same, so there will be no rotation or reflection.
ΔOAB gets dilated with origin as the centre of dilation to form ΔO'A'B'.
We will find the scale factor of the dilation. If it is greater than 1, then the dilation will be expansion, otherwise contraction.
The lengths of a pair of corresponding sides of the two triangles are calculated by the distance formula as follows:
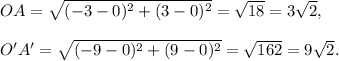
Therefore, the scale factor of the dilation is
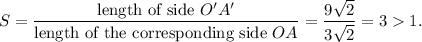
Since the scale factor is greater than 1, so the dilation will be expansion.
Thus, (A) is the correct option.