Answer:
Option (2)
Explanation:
Given functions are,
c(x) =
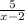
d(x) = x + 3
Equation of the composite function will be,
(cd)(x) = c(x) × d(x)
=
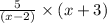
=
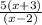
This function is defined only when denominator is not equal to zero.
(x - 2) ≠ 2
Therefore, for real numbers except x = 2 will be the domain of the composite function.
Option (2) will be the answer.