Answer:
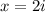
Explanation:
Given equation:
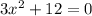
Factor 3 from the left side of the equation:
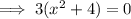
Divide both sides of the equation by 3:
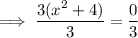
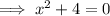
Subtract 4 from both sides:
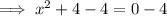
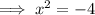
Square root both sides:
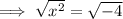
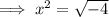
Rewrite -4 as 2² · -1:
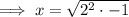
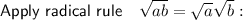
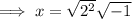
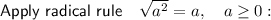
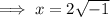
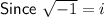
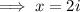
Imaginary numbers
Since there is no real number that squares to produce -1, the number
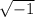 is called an imaginary number, and is represented using the letter i.
is called an imaginary number, and is represented using the letter i.
An imaginary number is written in the form
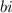 , where
, where
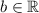 .
.