The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
A sample of nitrogen gas expands in volume from 1.6 to 5.4 L at constant temperature. Calculate the work done in joules if the gas expands (a) against a vacuum, (b) against a constant pressure of 0.80 atm, and (c) against a constant pressure of 3.7 atm. ( 1 L.atm = 101.3 J)
Answer:
For a: The work done for the given process is 0 J
For b: The work done for the given process is -308.04 J
For c: The work done for the given process is -1424.7 J
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the amount of work done for an isothermal process is given by the equation:
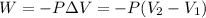 ......(1)
......(1)
W = amount of work done
P = pressure
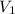 = initial volume
= initial volume
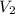 = final volume
= final volume
To convert this into joules, we use the conversion factor:
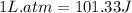
At vacuum, the pressure of the system will be 1 atm
We are given:
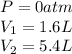
Putting values in above equation, we get:
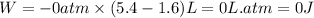
Hence, the work done for the given process is 0 J
We are given:
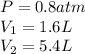
Putting values in above equation, we get:
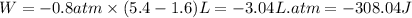
Hence, the work done for the given process is -308.04 J
We are given:
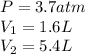
Putting values in above equation, we get:
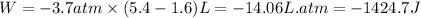
Hence, the work done for the given process is -1424.7 J