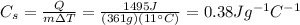When a certain amount of heat Q is absorbed by a substance, its temperature increases by

following the relationship
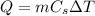
where m is the mass of the substance and
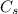
is the specific heat of the substance.
For the metal in our problem, the mass of the sample is m=361 g, the amount of heat is Q=1495 J, and the temperature difference is
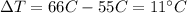
so by re-arranging the previous formula and by substituting the numbers we can find the specific heat of the metal: