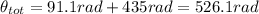Let's break the problem into two parts:
1) In the first part, the wheel starts with an angular speed
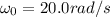
and it rotates with an angular acceleration of
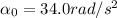
for t=1.80 s. So we can find the total angle covered by the wheel in this part of the motion:
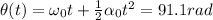
2) Now, the circuit breaker trips, so the wheel starts to decelerate with a certain angular acceleration
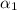
(which is negative). During this part of the motion, the wheel covered an angle of
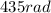
.
3) So, we just need to add the angles the wheel covered in the two parts of the motion: