First we need to find the voltage difference between the initial and final location of the electron.
Since the electron travelled for a distance d=5 m in an uniform electric field of intensity E=300 N/C, the voltage difference between the final and initial location is
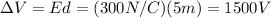
And then, we can calculate the change in potential energy of the electron, which is the product between the charge of the electron and the voltage difference:
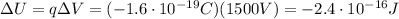
And the negative sign is due to the fact that we assumed the electron traveled in the natural direction of the electric field, so traveling from a point at lower voltage to a point at higher voltage (the sign of
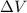
is positive), so since it's a negative charge the electron is losing potential energy.