The time t for a constant speed is given by:
t = distance/ velocity
Let's call the distance to run on the beach x₁ and the remaining distance to swim x₂, then the equation becomes:
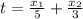
The distance x₂ depends on x₁:
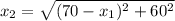
So:
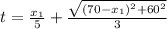
Find the minimum by setting the derivative to zero:
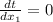
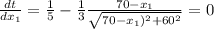
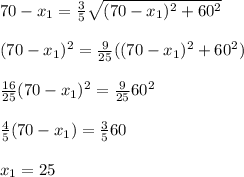
You should stop running 70m - 25m = 45m from b.