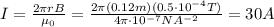The magnetic field generated by a wire carrying a current I is:
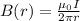
where r is the distance at which the magnetic field is measured, and
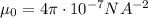
is the magnetic permeability in vacuum.
The problem says that the magnetic field at a distance r=12 cm=0.12 m from the wire must be no larger than
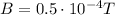
. Substituting these values, we can find the maximum value of the current I that the wire can carry: