Answer: Option (d) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
It is know that for an ideal gas PV = nRT
where P = pressure
V = volume
n = number of moles =
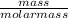
R = gas constant = 0.082
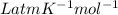
T = temperature
Therefore, put the given values in the formula above as follows.
PV = nRT
or, PV =
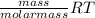
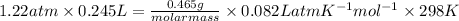
molar mass = 38.12 g/mol
= 38.0 g/mol (approx)
Therefore, we can conclude that the molar mass of the unknown compound is 38.0 g/mol.