Answer:
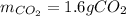
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, hexane's combustion is stood for the following chemical reaction:

Now, we need to identify the limiting reactant for which we compute both hexane's and oxygen's moles as shown below:
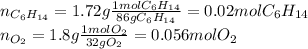
Afterwards, we compute the moles of hexane that completely react with 0.056 moles of oxygen via the stoichiometry:
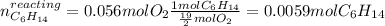
Now, since 0.02 moles of hexane are available but just 0.0059 moles react, the hexane is in excess and the oxygen is the limiting reactant, thus, the maximum mass of carbon dioxide is computed as shown below with two significant figures (due to the significant figures of the oxygen's initial mass) by using the moles of oxygen as the limiting reactant:
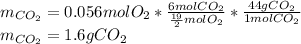
Best regards.