Answer:
The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter is -16,557.69 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of titanium = 1.000 g
Moles of titanium =
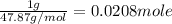
Heat capacity of the calorimeter ,c= 9.84 kJ/K
Initial temperature of the calorimeter ,T=25°C =298 K
Final temperature of the calorimeter ,T'= 60°C = 333 K
Heat gained by calorimeter = q
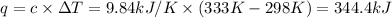
Heat of combustion released when 1 g of titanium = -344.4 kJ
Heat if released that is why negative sign is used.
In 1 g of titanium = 0.0208 mole
Heat of combustion of 0.0208 moles of titanium = -344.4 kJ
Heat of combustion of 1 moles of titanium:
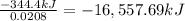
The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter is -16,557.69 kJ/mol.