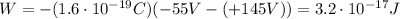The work done by the electric field in moving a charge is the negative of the potential energy difference between the two locations, which is the product between the magnitude of the charge q and the potential difference
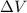
:
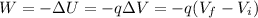
The proton charge is
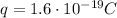
, and the two locations have potential of
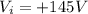
and
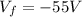
, therefore the work is