Step-by-step explanation:
Relation between freezing temperature and molal concentration is as follows.
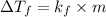
The given data is as follows.
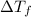 = difference in temperature =
= difference in temperature =
![[0 - (-2.75)]^(o)C](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/uonl6hxxgb3gkox6ywds2cuudw08kbcu48.png) =
=
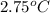
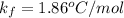
molality, (m) = ?
Now, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
m =
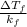
=
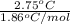
= 1.48 m
Therefore, we can conclude that molal concentration of glucose in the given solution is 1.48 m.