The total momentum of the system (astronaut+gas) must be conserved.
We can assume the astronaut is still before the gas starts to be ejected, therefore its speed is zero and its momentum is zero as well.
After the gas starts to be ejected, the total momentum of the system is:
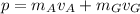
where
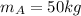
is the mass of the astronaut,
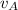
is the speed of the astronaut,
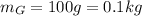
is the mass of the gas and
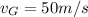
is the speed of the gas.
Since the momentum must be conserved, and the initial momentum was zero, then it must be
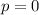
. Using this information, we can find the value of
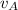
, the speed of the astronaut:
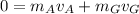
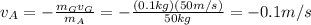
where the negative sign means that the astronaut starts to move in the opposite direction of the ejected gas.