Answer: Option (B) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
In a solid object, molecules are closely packed together due to strong intermolecular forces between them. So, when heat is provided to the object then forces between the atoms decreases and as a result, atoms start to move from their initial place.
Hence, atoms gain kinetic energy due to increase in their motion.
For example, when ice is heated it changes into liquid state of water.
Also, K.E =
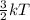
where k = Boltzmann constant
T = temperature
Hence, kinetic energy is directly proportional to temperature.
Thus, we can conclude that the temperature of an object is directly related to the motion of its particles.