Answer: 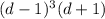
Step-by-step explanation:Let
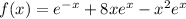
.
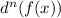
= nth derivative of f
Note that
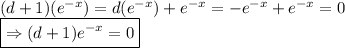
So, (d + 1) annihilates
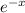
.
Note that
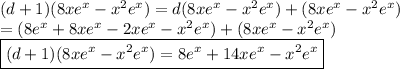
Let
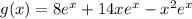
For any real number
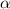
and positive integer n,
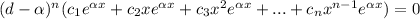
(1)
So, for g(x),
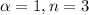
. Thus, using equation (1),
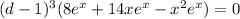
(2)
Since,
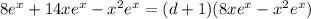
,
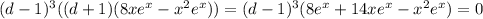
Moreover, since
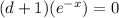
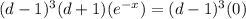
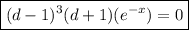
(3)
Hence based on equations (2) and (3),
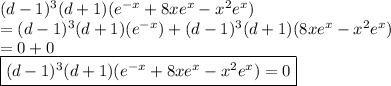
Therefore, the linear operator
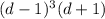 annihilates
annihilates
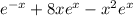 .
.