Answer:
False.
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rwpyhrof52dro5d128gleq5obchnuu5qkj.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Derivative Rule [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(g(x))] =f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vue68srn3fe6bds4idxorm97z7tgwelamw.png)
Integration
- Integrals
- Definite Integrals
- Integration Constant C
Integration Rule [Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 2]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[\int\limits^x_a {f(t)} \, dt] = f(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/idztrky79gppvnfr56mqizrybhxz594si6.png)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
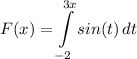
Step 2: Differentiate
- Chain Rule:
![\displaystyle F'(x) = (d)/(dx)[\int\limits^(3x)_(-2) {sin(t)} \, dt] \cdot (d)/(dx)[3x]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/o3ljlj4qlyeigpuggvu6z8ar7esp5k94a9.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle F'(x) = (d)/(dx)[\int\limits^(3x)_(-2) {sin(t)} \, dt] \cdot 3(d)/(dx)[x]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/zotdjv8ffr19x8gzvprc8c6ne1d96yc689.png)
- Basic Power Rule:
![\displaystyle F'(x) = (d)/(dx)[\int\limits^(3x)_(-2) {sin(t)} \, dt] \cdot 3x^(1 - 1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/kuyanozdxy71nm2u2ubwlsug1bvk3s7yx3.png)
- Simplify:
![\displaystyle F'(x) = 3(d)/(dx)[\int\limits^(3x)_(-2) {sin(t)} \, dt]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2jsqrpbc1oecmxvtly9auqyzrdev1aengi.png)
- Integration Rule [Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 2]:
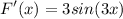
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Integration
Book: College Calculus 10e