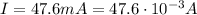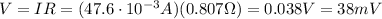First we need to calculate the resistance of this piece of wire. For a wire with resistivity
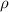
, length L and cross section A, the resistance is
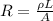
The diameter d of the wire is
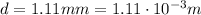
, so the cross sectional area is
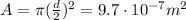
Now, using
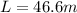
and
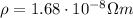
, we can calculate the resistance:
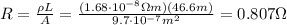
And now we can calculate the voltage drop across the resistor, by using Ohm's law, since we know the current flowing through it: