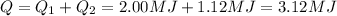We can solve the problem splitting in two steps.
1) First, we need to raise the temperature of the block of lead from
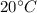
to its melting temperature (
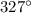
). The quantity of heat needed for this process is
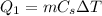
where
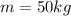
is the mass,
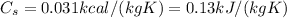
is the specific heat of lead, and
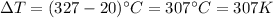
is the variation of temperature.
Calculating:
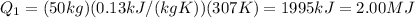
2) Once the block of lead has reached its melting temperature, we must add other heat to cause the complete fusion of the block. The amount of heat need in this process is
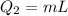
where
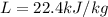
is the latent heat of fusion of lead. Therefore we have
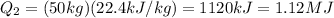
3) And so, the total amount of heat needed for the entire process is