- The voltage travelling away from a power plant through transmission lines is very high, and it is typically of hundreds of kilovolts (typical values are between 138 kV and 765 kV).
- The main reason to use these high values of voltage is to reduce power dissipation.
In fact, the cables that are used to transmit electricity have a certain resistance R which is fixed. The power generated from the power plant and that should be transmitted through the lines is P, and it is also fixed.
The power dissipated through the cables is calculated as
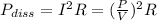
where I is the current and V the voltage.
As it can be seen, using higher voltages reduce the amount of power dissipated through the lines (while using higher currents will have the opposite effect).