Step-by-step explanation:
An oxidizing agent is defined as a substance which readily accepts an electron and itself gets reduced in order to oxidize another substance in a chemical reaction.
For example,
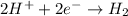
Here, hydrogen is getting reduced as its oxidation state is changing from +1 to 0 and hence it acts like an oxidizing agent.
In an oxidizing agent, a decrease in oxidation state occurs.
Whereas in
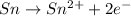 , tin is getting oxidized by gaining electrons. Therefore, it is acting as a reducing agent. An increase in oxidation state occurs for a reducing agent.
, tin is getting oxidized by gaining electrons. Therefore, it is acting as a reducing agent. An increase in oxidation state occurs for a reducing agent.
Thus, we can conclude that in the given reaction hydrogen is the oxidizing agent.