Answer : The final concentration was 0.199 M
Explanation :
The expression used for second order kinetics is:
![kt=(1)/([A_t])-(1)/([A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/y4nm4wqwe13w6z1i9no2ph0uajeawogjzq.png)
where,
k = rate constant =
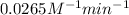
t = time = 180.0 min
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/fdhdda02dou33of7vmb5w1ohx8yyr25wdc.png) = final concentration = ?
= final concentration = ?
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/udsj4715666fnr0pmcxdb9w33wahmlplcn.png) = initial concentration = 4.25 M
= initial concentration = 4.25 M
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get:
![0.0265* 180.0=(1)/([A_t])-(1)/(4.25)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/pjjgs0ordpen7s4bw0r0i3icvgs9liyu8q.png)
![[A_t]=0.199M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/iumbuahrz9q6ak6f2if4hnna6colmt6kp0.png)
Therefore, the final concentration was 0.199 M